In the rapidly evolving landscape of B2B Software as a Service (SaaS), determining the optimal pricing model has become increasingly complex. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the SaaS landscape, coupled with a growing subscription fatigue among customers and a shift in investor focus from growth to profitability, is challenging traditional pricing strategies. This guide delves into the situation of B2B SaaS pricing models in 2025, examining their advantages, challenges, and suitability in the current market.

Why B2B SaaS pricing is changning
The impact of AI
The accessibility of AI radically changed the landscape of B2B SaaS. Countless AI driven SaaS products have emerged, offering enhanced automation, predictive analytics, and personalized user experiences. However, this advancement comes with significant costs. AI models demand substantial computational resources, leading to increased operational expenses for providers. Consequently, pricing strategies must account for these elevated costs while remaining attractive to customers.
Subscription fatigue
As the SaaS market matures, customers have adopted numerous subscription-based services, leading to subscription fatigue. Businesses are looking to cut costs and consolidate their subscription-based services, seeking flexible and transparent pricing models that align with their actual usage and deliver clear value. This shift forces SaaS providers to rethink their pricing strategies to maintain competitiveness and customer satisfaction.
Investor focus on profitability
In recent years, venture capitalists and investors have shifted their focus from pure growth metrics to sustainable profitability. This change pressures SaaS companies to adopt pricing models that not only drive customer acquisition but also ensure long-term financial health. Balancing competitive pricing with profitability has become a critical challenge in the current investment climate.
Popular B2B SaaS pricing models in 2025
1. Flat-Rate Pricing
Flat-rate pricing offers a single, unvarying price for access to the SaaS product, regardless of usage intensity.
Advantages:
- Simplicity and transparency: Customers appreciate the straightforward nature of flat-rate pricing, which eliminates unexpected costs and simplifies budgeting.
- Predictable revenue: Providers benefit from consistent, predictable income streams, facilitating financial planning and stability.
Challenges:
- Limited flexibility: This model may not accommodate the diverse needs of all customers, potentially leading to overpricing for light users and underpricing for heavy users.
- Competitive pressure: In a market trending towards usage-based models, flat-rate pricing may appear less attractive to cost-conscious customers.
Despite being considered traditional, flat-rate pricing remains prevalent among established SaaS companies. For instance, Stripe has introduced a flat-rate pricing model for its billing solution, providing an alternative to its usage-based pricing.
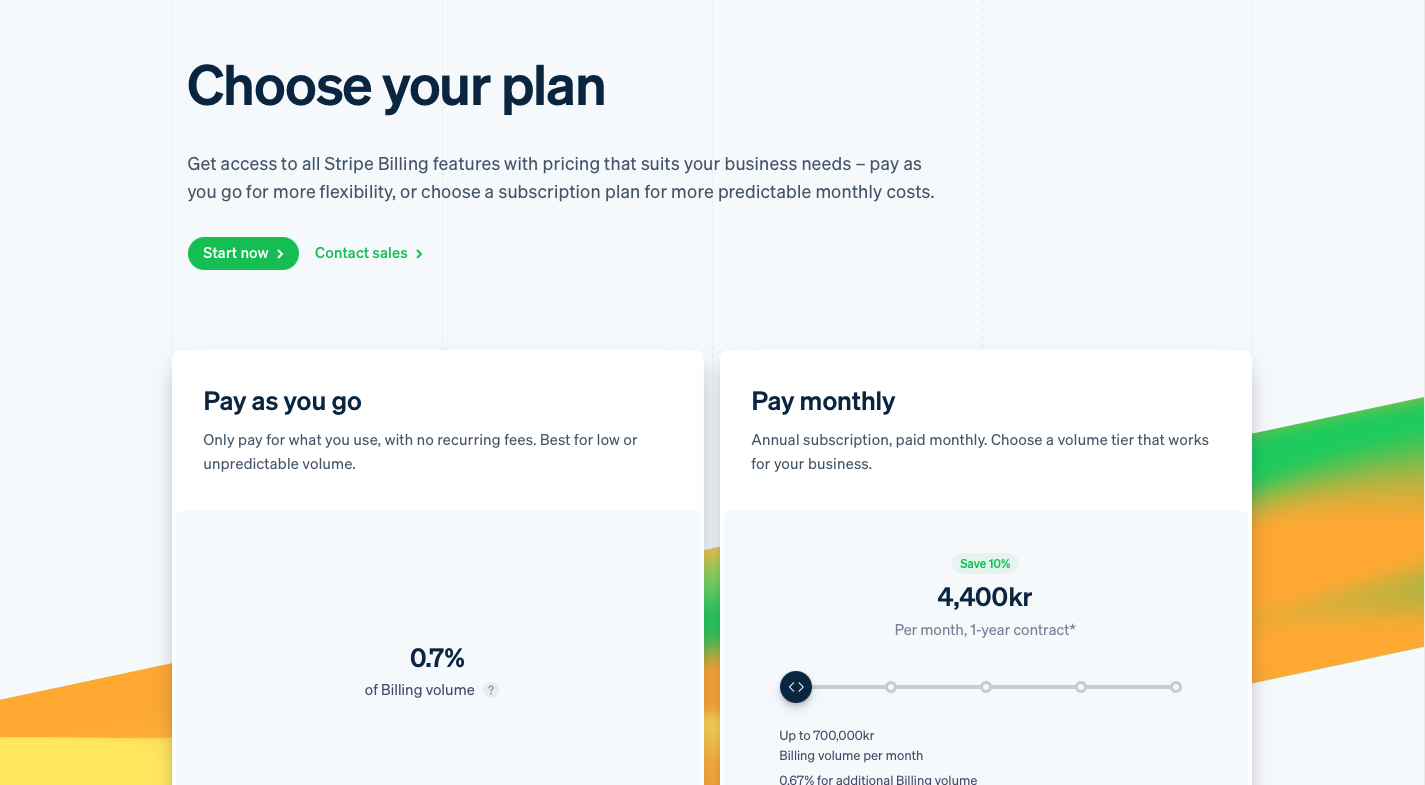 Stripe billing flat-rate alternative to usage-based pricing.
Stripe billing flat-rate alternative to usage-based pricing.
2. Freemium pricing
The freemium model offers a basic version of the product at no cost, with premium features available through paid subscriptions.
Advantages:
- Customer acquisition: By lowering the barrier to entry, freemium models attract a broad user base, allowing potential customers to experience the product before committing financially.
- Product-Led Growth (PLG): This approach leverages the product itself as the primary driver of customer acquisition and retention, fostering organic growth.
Challenges:
- Conversion rates: Transitioning users from free to paid plans can be challenging, requiring compelling premium features and strategic marketing.
- Cost management: Supporting a large base of free users incurs operational costs, which must be balanced against the revenue from paid subscribers.
The freemium model continues to thrive, especially with the rise of Product-Led Growth (PLG) strategies. Companies utilize this model to build user communities and drive engagement, with the goal of converting a portion of free users into paying customers.
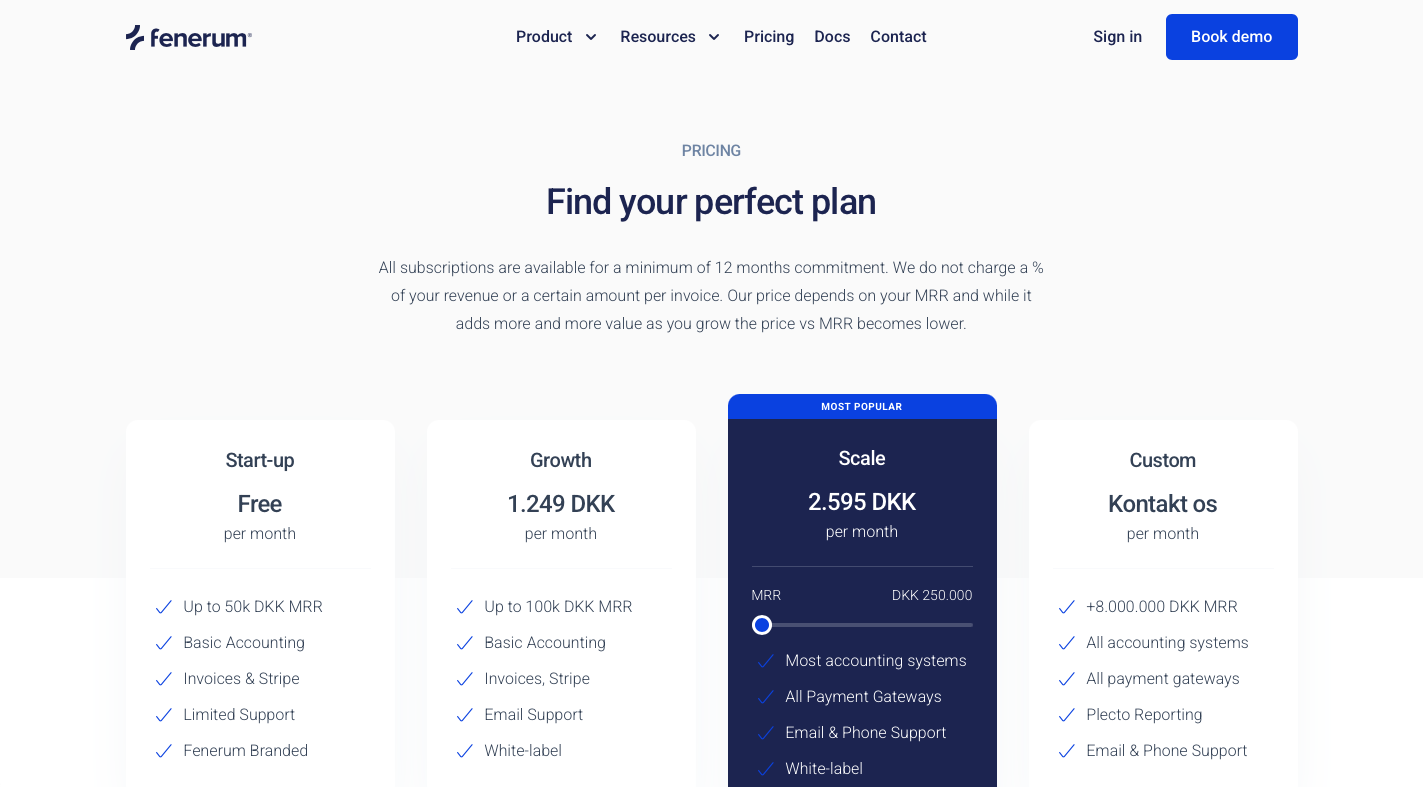 Fenerum freemium plan option.
Fenerum freemium plan option.
3. Tiered pricing
Tiered pricing offers multiple packages with varying features and price points, allowing customers to select the option that best fits their needs.
Advantages:
- Customization: This model caters to a wide range of customers, from small businesses to large enterprises, by providing options that align with different requirements and budgets.
- Revenue optimization: By segmenting features and services, providers can encourage customers to choose higher-priced tiers that offer greater value.
Challenges:
- Complexity: Managing multiple tiers requires careful structuring to ensure clarity and avoid customer confusion.
- Resource allocation: Providers must balance the development and support resources across different tiers to maintain service quality.
Tiered pricing is widely adopted in the SaaS industry, enabling companies to appeal to diverse market segments and maximize revenue potential.
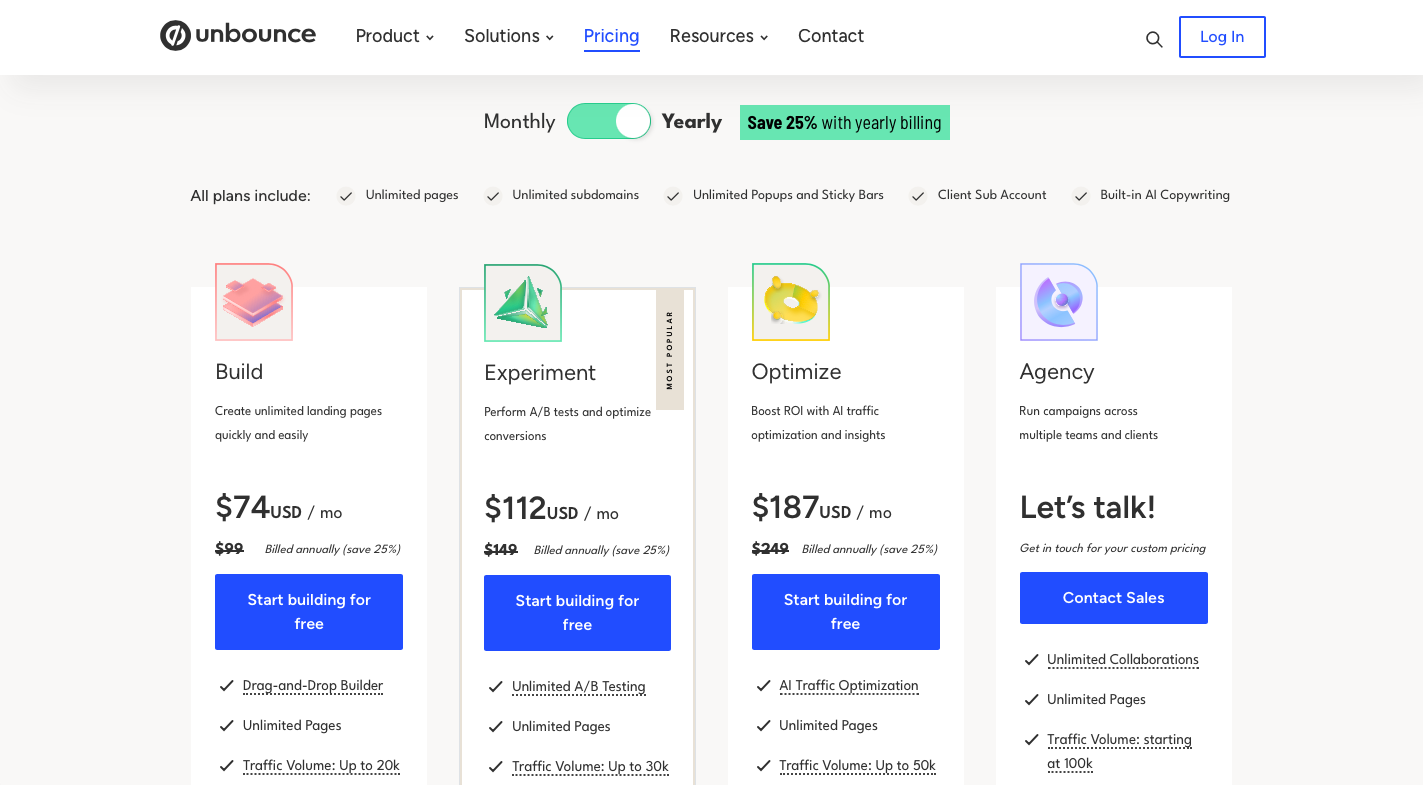 Unbounce tiered pricing plan option.
Unbounce tiered pricing plan option.
4. Usage-based pricing
Also known as consumption-based pricing, this model charges customers based on their actual usage of the product or service.
Advantages:
- Alignment with value: Customers pay in proportion to the value they derive, making this model attractive to those seeking cost efficiency.
- Scalability: Usage-based pricing accommodates growth, allowing costs to scale with the customer's business.
Challenges:
- Revenue predictability: For providers, income can fluctuate based on customer usage patterns, complicating financial forecasting.
- Customer uncertainty: Variable costs may lead to budgeting challenges for customers, potentially deterring adoption.
The rise of AI has propelled the popularity of usage-based pricing models. Companies are exploring this approach to offer flexibility and align costs with consumption. However, debates persist regarding revenue recognition and the classification of such income as Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR).
 OpenAI usage-based billing plan option.
OpenAI usage-based billing plan option.
Conclusion
The landscape of B2B SaaS pricing models is changing and providers must navigate the evolving market dynamics, including the impact of AI, subscription fatigue, and investor expectations, to develop pricing strategies that drive growth and profitability. B2B SaaS companies will increasingly be required to rethink their pricing models and offer flexible, value-driven solutions that cater to the diverse and changing needs of customers. For more insights on B2B SaaS pricing and subscription management, visit Fenerum and explore our comprehensive resources.
