What is SaaS?
So, what is SaaS? SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a cloud-based service where applications are hosted by a third-party provider and made available to customers over the internet as a service. This business model allows users or customers to access the application through a web browser without the hassle of installing or managing hardware and software.
A SaaS company like Salesforce is often credited as one of the pioneers of the SaaS model. The success of Salesforce and other early SaaS companies demonstrated the viability and benefits of the SaaS model, leading to its rapid growth. Today, SaaS is a cornerstone of the software industry, with applications spanning numerous business functions and industries. McKinsey estimates that the SaaS market will be worth $10 trillion by 2030. Some notable examples of successful SaaS companies are Salesforce, Slack, Figma, Netflix, Spotify, and so on.
Key Benefits of SaaS
- Accessibility: Users can access SaaS applications from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Scalability: SaaS solutions can easily scale to accommodate the growing needs for a service.
- Subscription-Based: Typically, SaaS is offered on a subscription basis, offering a continues revenue stream.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Subscription-based pricing models reduce the need for significant upfront investments.
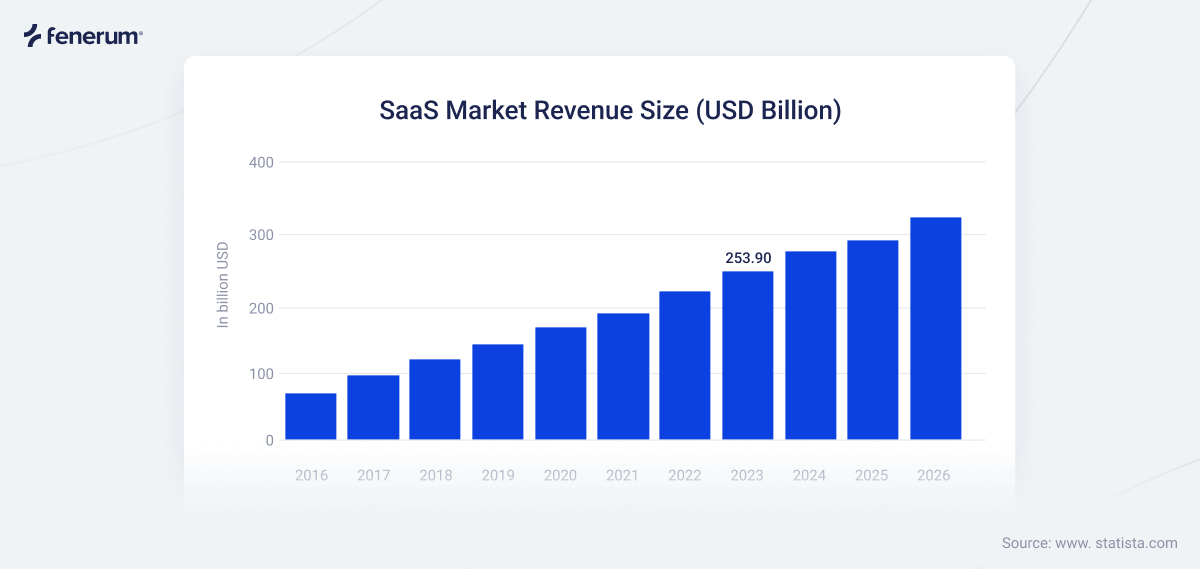 Global SaaS Market Revenue Size from 2016-2026 according to Statista. updated July 2024.
Global SaaS Market Revenue Size from 2016-2026 according to Statista. updated July 2024.
SaaS vs. IaaS and PaaS
While SaaS is a popular model, it is just one of several cloud-based models, which include Infrastructure as a Service ( IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS). Understanding the differences between these models is essential when choosing a service provider or when choosing a model for your own business.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It allows businesses to rent infrastructure components such as servers, storage, and networking hardware, offering flexibility and control over their IT resources. Examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure. This model includes tools and services for application development, making it easier for developers to focus on writing code and delivering applications. Google App Engine and Heroku are well-known PaaS providers.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
In contrast to IaaS and PaaS, SaaS delivers fully functional software applications via a web browser. Businesses using SaaS don’t need to worry about managing hardware, software updates, or security patches, as these are handled by the SaaS provider. Popular SaaS companies include Salesforce, Google Workspace, and Zoom.
SaaS Pricing Models
One of the defining features of Software as a Service is its flexible pricing models. These models are designed to make software accessible and affordable for businesses of all sizes:
Freemium Pricing
The freemium model provides a basic or limited version of the software for free, with the option to upgrade to a paid version for additional features and capabilities. This is a popular option offered by SaaS companies as it allows users to try the software before committing to a subscription. Some SaaS providers offer this 'freemium' solution as a lifetime deal, while others offer it for a limited time. However, this is almost always with the intention of converting freemium customers to paying customers within a specific period.
Subscription-Based Pricing
Most SaaS companies use a subscription-based pricing model, where customers pay a recurring fee (monthly or annually) to use the software. This model is often based on different tiers such as features, users, contracts, usage, revenue, or even MRR. An example could be a SaaS CRM solution that offers a 'starter' subscription with up to 5 users at €29 per month or a 'pro' subscription that offers unlimited users at €99 per month. This would be a typical subscription-based pricing model.
This type of tiered subscription-based pricing model allows customers to choose the subscription that fits their needs and further allows them to grow with the tool as their business grows and expands. Get inspired by our pricing model here.
Enterprise Pricing
The subscription-based pricing model is a good solution for small and medium-sized companies; however, larger organizations might have more complex needs. For larger organizations, many SaaS providers offer custom enterprise pricing. This is tailored to the specific needs and scale of the enterprise, often including volume discounts, premium support, and additional services.
Conclusion
The Software as a Service (SaaS) model has transformed the business landscape of how we manage software applications. SaaS providers offer cost-effective, scalable, and easily accessible solutions, enabling companies to focus on their core activities without the hassle of managing complex and time-consuming IT infrastructure. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, embracing SaaS can drive efficiency, innovation, and growth.
Understanding the meaning of SaaS and the differences between IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS can help businesses make informed decisions about adopting SaaS solutions. As the software landscape continues to evolve, SaaS remains a growing and expanding market that you need to keep your eye on!
